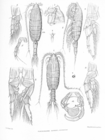
WoRMS taxon details
Pleuromamma xiphias (Giesbrecht, 1889)
104643 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:104643)
accepted
Species
Pleuromma xiphias Giesbrecht, 1889 · unaccepted (synonym)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
Giesbrecht, W. (1899). Die Asterocheriden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres- Abschnitte. The Asterocherids of the Gulf of Naples and the adjacent marine areas. <em>Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapel und der Angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte, Herausgegeben von der Zoologischen Station zu Neapel.</em> 25:i-vi, 1-217, pls. 1-11. [details] 
(of Pleuromma xiphias Giesbrecht, 1889) Giesbrecht, W. (1899). Die Asterocheriden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres- Abschnitte. The Asterocherids of the Gulf of Naples and the adjacent marine areas. <em>Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapel und der Angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte, Herausgegeben von der Zoologischen Station zu Neapel.</em> 25:i-vi, 1-217, pls. 1-11.
page(s): 25 [details]
(of Pleuromma xiphias Giesbrecht, 1889) Giesbrecht, W. (1899). Die Asterocheriden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres- Abschnitte. The Asterocherids of the Gulf of Naples and the adjacent marine areas. <em>Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapel und der Angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte, Herausgegeben von der Zoologischen Station zu Neapel.</em> 25:i-vi, 1-217, pls. 1-11.
page(s): 25 [details]
Distribution Cosmopolitan except for Arctic
Distribution Cosmopolitan except for Arctic [details]
Walter, T.C.; Boxshall, G. (2025). World of Copepods Database. Pleuromamma xiphias (Giesbrecht, 1889). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=104643 on 2025-07-17
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
Nomenclature
original description
Giesbrecht, W. (1899). Die Asterocheriden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres- Abschnitte. The Asterocherids of the Gulf of Naples and the adjacent marine areas. <em>Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapel und der Angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte, Herausgegeben von der Zoologischen Station zu Neapel.</em> 25:i-vi, 1-217, pls. 1-11. [details] 
original description (of Pleuromma xiphias Giesbrecht, 1889) Giesbrecht, W. (1899). Die Asterocheriden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres- Abschnitte. The Asterocherids of the Gulf of Naples and the adjacent marine areas. <em>Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapel und der Angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte, Herausgegeben von der Zoologischen Station zu Neapel.</em> 25:i-vi, 1-217, pls. 1-11.
page(s): 25 [details]
basis of record Boxshall, G. (2001). Copepoda (excl. Harpacticoida), <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 252-268 (look up in IMIS) [details]
original description (of Pleuromma xiphias Giesbrecht, 1889) Giesbrecht, W. (1899). Die Asterocheriden des Golfes von Neapel und der angrenzenden Meeres- Abschnitte. The Asterocherids of the Gulf of Naples and the adjacent marine areas. <em>Fauna und Flora des Golfes von Neapel und der Angrenzenden Meeres-Abschnitte, Herausgegeben von der Zoologischen Station zu Neapel.</em> 25:i-vi, 1-217, pls. 1-11.
page(s): 25 [details]
basis of record Boxshall, G. (2001). Copepoda (excl. Harpacticoida), <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 252-268 (look up in IMIS) [details]
Ecology
ecology source
Brun, P., M.R. Payne & T. Kiørboe. (2017). A trait database for marine copepods. <em>Earth System Science Data.</em> 9(1):99-113., available online at https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-99-2017 [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
Other
context source (Deepsea)
Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
context source (Bermuda) Wilson, C. B. (1936). Plankton of the Bermuda Oceanographic Expeditions IV. Notes on Copepoda . Zoologica Scientific Contributions of the New York Zoological Society , New York, 21(7): 89-93 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Grice, G.D. & K. Hulsemann. (1967). Bathypelagic calanoid copepods of the western Indian Ocean. <em>Proceedings of the United States National Museum.</em> 122(3583):1-67, figs. 1-319., available online at https://doi.org/10.5479/si.00963801.122-3583.1 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Arcos, D.F. (1975). Copépodes calanoídeos de la Bahía de Concepción, Chile. Conocimiento sistemático y variación estacional. [Calanoid Copepods of the Concepcion Bay, Chile, Systematic study and seasonal variation.]. <em>Gayana, Zoología.</em> 32:3-31, figs. 1-7, pls. 1-9 with figs. 1-78, map. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Bannister, N.J. & P.J. Herring. (1989). Distribution and structure of luminous cells in four marine copepods. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 69(3):523-533, figs. 1-5. (viii.1989) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Bradford-Grieve, J.M. (1999). The Marine Fauna of New Zealand: Pelagic Calanoid Copepoda: Bathypontiidae, Arietellidae, Augaptilidae, Heterorhabdidae, Lucicutiidae, Metrodinidae, Phyllopodidae, Centropagidae, Pseudodiaptomidae, Temoridae, Candaciidae, Pontellidae, Sulcanidae, Acartiid National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA) Biodiversity Memoir, Wellington 111:1-268. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Buskey, E.J., K.S. Baker, R.C. Smith & E. Swift. (1989). Photosensitivity of the oceanic copepods Pleuromamma gracilis and Pleuromamma xiphias and its relationship to light penetration and daytime depth distribution. Marine Ecology Progress Series 55(2):207-216. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Chiba, T. (1956). Studies on the development and the systematics of Copepoda. Journal of the Shimonoseki College of Fisheries 6(1):1-90. (xi-1956). (In Japanese, English summary.) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Ferrari, F.D. (1985). Postnaupliar development of a looking-glass copepod, Pleuromamma xiphias (Giesbrecht, 1889), with analyses of distributions of sex and asymmetry. Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology 420:i-iii, 1-55, figs. 1-23. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Ferrari, F.D. & A. Benforado. (1998). Relationships between arthrodial membrane formation and addition of setae to swimming legs 1-4 during development of Dioithona oculata, Ridgewayia klausruetzleri, Pleuromamma xiphias, and Temora longicornis (Copepoda). Crustaceana, Leiden 71(5):545-564. (vii.1998) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Ferrari, F.D. & A. Benforado. (1998). Setation and setal groups on antenna 1 of Ridgewayia klausreutzleri, Pleuromamma xiphias, and Pseudocalanus elongatus (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) during the copepodid phase of their development. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 111(1):209-221. (6.iv.1998) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Ferrari, F.D. & L.A.C. Hayek. (1990). Monthly differences in distributions of sex and asymmetry in a looking-glass copepod, Pleuromamma xiphias, off Hawaii. Journal of Crustacean Biology 10(1):114-127. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Fields, D.M. & J. Yen. (1996). The escape behavior of Pleuromamma xiphias from a quantifiable fluid mechanical disturbance. Chapter 3. <em>In: Lenz, P.H., D.K. Hartline, J.E. Purcell & D.L. Macmillan (eds.). Zooplankton: Sensory Ecology and Physiology. Vol. 1. Gordan and Breach Publishers, Amsterdam.</em> :323-340. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source ICES Zooplankton: Copepoda. sheet n° 32. [details]
additional source Scott, A. (1909). The Copepoda of the Siboga Expedition. Part I. Free-swimming, littoral and semi-parasitic Copepoda. <em>Siboga Expeditie, Monograph, Leiden.</em> 29:1-323, pls. 1-69., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/2191407#page/11/mode/1up
page(s): 124 [details]
additional source Wilson, C.B. (1932). The copepods of the Woods Hole region, Massachusetts. <em>Bulletin of the United States National Museum.</em> 158:1-635, figs. 1-316, pls. 1-41. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Jeong, H.G., S.J. Lee & H.Y. Soh. (2022). First Record of Three Pleuromamma Species (Copepoda: Calanoida: Metridinidae) in Korea. <em>Animal Systematics Evolution and Diversity.</em> 38(1):1-13. Jan 2022. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Latz, M.I., T.M. Frank, M.R. Bowlby, M.R. Widder & J.F. Case. (1987). Variability in flash characteristics of a bioluminescent copepod. Biological Bulletin, Woods Hole 173(3):489-503, figs. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Lenz, P.H., T.M. Weatherby, W. Weber & K.K. Wong. (1996). Sensory specialization along the first antenna of a calanoid copepod Pleuromamma xiphias (Crustacea). <em>Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology.</em> 27(2-3):213-221., available online at https://doi.org/10.1080/10236249609378966 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Park, J.S. (1995). The development of integumental pore signatures in the Genus Pleuromamma (Copepoda: Calanoida). <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom.</em> 75(1):211-218. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Saraswathy, M. (1986). Pleuromamma (Copepoda-Calanoida) in the Indian Ocean. Mahasagar, Goa 19(3):185-201. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Sewell, R.B.S. (1932). The Copepoda of Indian Seas. Calanoida. <em>Memoirs of the Indian Museum, Calcutta.</em> 10:223-407, figs. 82-131, pls. 1-6. (xii-1929, v-1932). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Steuer, A. (1932). Copepoda (6). Pleuromamma Giesbr. 1898 der Deutschen Tiefsee Expedition. Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse der Deutschen Tiefsee-Expedition 'Valdivia' 24:1-119, fig. 1-196, maps 1-17. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Tanaka, O. (1963). The pelagic copepods of the Izu region, Middle Japan. Systematic account IX. Families Centropagidae, Pseudodiaptomidae, Temoridae, Metridiidae and Lucicutiidae. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory 11(1):7-55, figs. 152-174. (20-vii-1963) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Vervoort, W. (1965). Pelagic Copepoda. Part II. Copepoda Calanoida of the families Phaennidae up to and including Acartiidae, containing the description of a new species of Aetideidae. Atlantide Report, Danish Expedition to Coasts of Tropical West Africa 1945-1946 8:9-216. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Weatherby, T.M., K.K. Wong & P.H. Lenz. (1994). Fine structure of the distal sensory setae on the first antennae of Pleuromamma xiphias Giesbrecht (Copepoda). Journal of Crustacean Biology 14(4):670-685, figs 1-7, tab. 1. (01.xi.1994) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Webber, W.R., G.D. Fenwick, J.M. Bradford-Grieve, S.G. Eagar, J.S. Buckeridge, G.C.B. Poore, E.W. Dawson, L. Watling, J.B. Jones, J.B.J. Wells, N.L. Bruce, S.T. Ahyong, K. Larsen, M.A. Chapman, J. Olesen, J.S. Ho, J.D. Green, R.J. Shiel, C.E.F. Rocha, A. Lörz, G.J. Bird & W.A. Charleston. (2010). Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum Crustacea: shrimps, crabs, lobsters, barnacles, slaters, and kin. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2010). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 2. Kingdom Animalia: Chaetognatha, Ecdysozoa, Ichnofossils.</em> pp. 98-232 (COPEPODS 21 pp.). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Suárez-Morales, E., J.W. Fleeger & P.A. Montagna. (2009). Free-living Copepoda (Crustacea) of the Gulf of Mexico. <em>In: Felder, D. L. & D.K. Camp [Eds]. Gulf of Mexico: origin, waters, and biota. Volume 1, Biodiversity. Texas A&M University Press, 1393 pp.</em> Chapter pagination: 841-869. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Prusova, I.Y., S.L. Smith & E. Popova. 2012. Calanoid copepods of the Arabian Sea region. Sultan Qaboos University, Academic Publication Board, Muscat, Oman 240 pp., 240 figs. (2011). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Lee, B.D. (1966). Distribution and abundance of pelagic copepods in the Drake Passage and off the coast of Argentina, with special reference to hydrology of these areas. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, 1-250, pls. 1-56. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
context source (Bermuda) Wilson, C. B. (1936). Plankton of the Bermuda Oceanographic Expeditions IV. Notes on Copepoda . Zoologica Scientific Contributions of the New York Zoological Society , New York, 21(7): 89-93 [details] Available for editors
additional source Grice, G.D. & K. Hulsemann. (1967). Bathypelagic calanoid copepods of the western Indian Ocean. <em>Proceedings of the United States National Museum.</em> 122(3583):1-67, figs. 1-319., available online at https://doi.org/10.5479/si.00963801.122-3583.1 [details] Available for editors
additional source Arcos, D.F. (1975). Copépodes calanoídeos de la Bahía de Concepción, Chile. Conocimiento sistemático y variación estacional. [Calanoid Copepods of the Concepcion Bay, Chile, Systematic study and seasonal variation.]. <em>Gayana, Zoología.</em> 32:3-31, figs. 1-7, pls. 1-9 with figs. 1-78, map. [details] Available for editors
additional source Bannister, N.J. & P.J. Herring. (1989). Distribution and structure of luminous cells in four marine copepods. Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom 69(3):523-533, figs. 1-5. (viii.1989) [details] Available for editors
additional source Bradford-Grieve, J.M. (1999). The Marine Fauna of New Zealand: Pelagic Calanoid Copepoda: Bathypontiidae, Arietellidae, Augaptilidae, Heterorhabdidae, Lucicutiidae, Metrodinidae, Phyllopodidae, Centropagidae, Pseudodiaptomidae, Temoridae, Candaciidae, Pontellidae, Sulcanidae, Acartiid National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA) Biodiversity Memoir, Wellington 111:1-268. [details] Available for editors
additional source Buskey, E.J., K.S. Baker, R.C. Smith & E. Swift. (1989). Photosensitivity of the oceanic copepods Pleuromamma gracilis and Pleuromamma xiphias and its relationship to light penetration and daytime depth distribution. Marine Ecology Progress Series 55(2):207-216. [details] Available for editors
additional source Chiba, T. (1956). Studies on the development and the systematics of Copepoda. Journal of the Shimonoseki College of Fisheries 6(1):1-90. (xi-1956). (In Japanese, English summary.) [details] Available for editors
additional source Ferrari, F.D. (1985). Postnaupliar development of a looking-glass copepod, Pleuromamma xiphias (Giesbrecht, 1889), with analyses of distributions of sex and asymmetry. Smithsonian Contributions to Zoology 420:i-iii, 1-55, figs. 1-23. [details] Available for editors
additional source Ferrari, F.D. & A. Benforado. (1998). Relationships between arthrodial membrane formation and addition of setae to swimming legs 1-4 during development of Dioithona oculata, Ridgewayia klausruetzleri, Pleuromamma xiphias, and Temora longicornis (Copepoda). Crustaceana, Leiden 71(5):545-564. (vii.1998) [details] Available for editors
additional source Ferrari, F.D. & A. Benforado. (1998). Setation and setal groups on antenna 1 of Ridgewayia klausreutzleri, Pleuromamma xiphias, and Pseudocalanus elongatus (Crustacea: Copepoda: Calanoida) during the copepodid phase of their development. Proceedings of the Biological Society of Washington 111(1):209-221. (6.iv.1998) [details] Available for editors
additional source Ferrari, F.D. & L.A.C. Hayek. (1990). Monthly differences in distributions of sex and asymmetry in a looking-glass copepod, Pleuromamma xiphias, off Hawaii. Journal of Crustacean Biology 10(1):114-127. [details] Available for editors
additional source Fields, D.M. & J. Yen. (1996). The escape behavior of Pleuromamma xiphias from a quantifiable fluid mechanical disturbance. Chapter 3. <em>In: Lenz, P.H., D.K. Hartline, J.E. Purcell & D.L. Macmillan (eds.). Zooplankton: Sensory Ecology and Physiology. Vol. 1. Gordan and Breach Publishers, Amsterdam.</em> :323-340. [details] Available for editors
additional source ICES Zooplankton: Copepoda. sheet n° 32. [details]
additional source Scott, A. (1909). The Copepoda of the Siboga Expedition. Part I. Free-swimming, littoral and semi-parasitic Copepoda. <em>Siboga Expeditie, Monograph, Leiden.</em> 29:1-323, pls. 1-69., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/2191407#page/11/mode/1up
page(s): 124 [details]
additional source Wilson, C.B. (1932). The copepods of the Woods Hole region, Massachusetts. <em>Bulletin of the United States National Museum.</em> 158:1-635, figs. 1-316, pls. 1-41. [details] Available for editors
additional source Jeong, H.G., S.J. Lee & H.Y. Soh. (2022). First Record of Three Pleuromamma Species (Copepoda: Calanoida: Metridinidae) in Korea. <em>Animal Systematics Evolution and Diversity.</em> 38(1):1-13. Jan 2022. [details] Available for editors
additional source Latz, M.I., T.M. Frank, M.R. Bowlby, M.R. Widder & J.F. Case. (1987). Variability in flash characteristics of a bioluminescent copepod. Biological Bulletin, Woods Hole 173(3):489-503, figs. [details] Available for editors
additional source Lenz, P.H., T.M. Weatherby, W. Weber & K.K. Wong. (1996). Sensory specialization along the first antenna of a calanoid copepod Pleuromamma xiphias (Crustacea). <em>Marine and Freshwater Behaviour and Physiology.</em> 27(2-3):213-221., available online at https://doi.org/10.1080/10236249609378966 [details] Available for editors
additional source Park, J.S. (1995). The development of integumental pore signatures in the Genus Pleuromamma (Copepoda: Calanoida). <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of the United Kingdom.</em> 75(1):211-218. [details] Available for editors
additional source Saraswathy, M. (1986). Pleuromamma (Copepoda-Calanoida) in the Indian Ocean. Mahasagar, Goa 19(3):185-201. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sewell, R.B.S. (1932). The Copepoda of Indian Seas. Calanoida. <em>Memoirs of the Indian Museum, Calcutta.</em> 10:223-407, figs. 82-131, pls. 1-6. (xii-1929, v-1932). [details] Available for editors
additional source Steuer, A. (1932). Copepoda (6). Pleuromamma Giesbr. 1898 der Deutschen Tiefsee Expedition. Wissenschaftliche Ergebnisse der Deutschen Tiefsee-Expedition 'Valdivia' 24:1-119, fig. 1-196, maps 1-17. [details] Available for editors
additional source Tanaka, O. (1963). The pelagic copepods of the Izu region, Middle Japan. Systematic account IX. Families Centropagidae, Pseudodiaptomidae, Temoridae, Metridiidae and Lucicutiidae. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory 11(1):7-55, figs. 152-174. (20-vii-1963) [details] Available for editors
additional source Vervoort, W. (1965). Pelagic Copepoda. Part II. Copepoda Calanoida of the families Phaennidae up to and including Acartiidae, containing the description of a new species of Aetideidae. Atlantide Report, Danish Expedition to Coasts of Tropical West Africa 1945-1946 8:9-216. [details] Available for editors
additional source Weatherby, T.M., K.K. Wong & P.H. Lenz. (1994). Fine structure of the distal sensory setae on the first antennae of Pleuromamma xiphias Giesbrecht (Copepoda). Journal of Crustacean Biology 14(4):670-685, figs 1-7, tab. 1. (01.xi.1994) [details] Available for editors
additional source Webber, W.R., G.D. Fenwick, J.M. Bradford-Grieve, S.G. Eagar, J.S. Buckeridge, G.C.B. Poore, E.W. Dawson, L. Watling, J.B. Jones, J.B.J. Wells, N.L. Bruce, S.T. Ahyong, K. Larsen, M.A. Chapman, J. Olesen, J.S. Ho, J.D. Green, R.J. Shiel, C.E.F. Rocha, A. Lörz, G.J. Bird & W.A. Charleston. (2010). Phylum Arthropoda Subphylum Crustacea: shrimps, crabs, lobsters, barnacles, slaters, and kin. <em>in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2010). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 2. Kingdom Animalia: Chaetognatha, Ecdysozoa, Ichnofossils.</em> pp. 98-232 (COPEPODS 21 pp.). [details] Available for editors
additional source Suárez-Morales, E., J.W. Fleeger & P.A. Montagna. (2009). Free-living Copepoda (Crustacea) of the Gulf of Mexico. <em>In: Felder, D. L. & D.K. Camp [Eds]. Gulf of Mexico: origin, waters, and biota. Volume 1, Biodiversity. Texas A&M University Press, 1393 pp.</em> Chapter pagination: 841-869. [details] Available for editors
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Prusova, I.Y., S.L. Smith & E. Popova. 2012. Calanoid copepods of the Arabian Sea region. Sultan Qaboos University, Academic Publication Board, Muscat, Oman 240 pp., 240 figs. (2011). [details] Available for editors
additional source Lee, B.D. (1966). Distribution and abundance of pelagic copepods in the Drake Passage and off the coast of Argentina, with special reference to hydrology of these areas. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, Texas, 1-250, pls. 1-56. [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From regional or thematic species database
Distribution Cosmopolitan except for Arctic [details]Unreviewed
Habitat Known from seamounts and knolls [details]
Marine Planktonic Copepods (Banyuls/OOB/UPMC/CNRS) Note: Including taxonomic identification plates, remarks, geographic distribution, ecological information & reference list
To Barcode of Life (211 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (32 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Pleuromamma xiphias)
To GenBank (378 nucleotides; 344 proteins)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (76 records)
To ITIS
To Barcode of Life (211 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (32 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Pleuromamma xiphias)
To GenBank (378 nucleotides; 344 proteins)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI)
To PESI
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (76 records)
To ITIS